The Art of Strategic Gameplay: Turn-Based Games
In the vast landscape of gaming, turn-based games stand out as a unique genre that demands cunning strategy and careful planning. From classic board games like chess to immersive digital experiences, turn-based games have captured the hearts of players worldwide. In layman’s terms, Turn-based games are a genre of video games that require players to take turns when performing actions, such as moving, attacking, or using items. But unlike real-time games, where events happen continuously and simultaneously, turn-based games allow players to plan their moves carefully and execute them at their own pace. This genre of games is often associated with strategy and role-playing games, but they can also be found in other genres, such as puzzle, board, card, and simulation games. It’s essential to understand the distinction between roguelike and roguelite games. Traditionally, roguelike games were defined by their turn-based gameplay, grid-based movement, and permanent character death, among other characteristics. These games were often known for their high difficulty, complex systems, and deep mechanics. On the other hand, roguelite games take inspiration from roguelikes but incorporate certain modifications and additions. While they retain elements like procedurally generated levels and permadeath, roguelites introduce more forgiving mechanics, such as persistent progression, unlockable upgrades, and a stronger focus on action-oriented gameplay. This subtle shift opens up the genre to a wider audience, making it more accessible and engaging for players who may not be accustomed to the extreme challenge of traditional roguelikes. What is a turn-based game? For a more specific definition, a TBG or turn-based game is a game that divides the gameplay into discrete segments or phases called turns. Each turn, one or more players (or computer-controlled entities) can perform a limited number of actions, such as moving on a grid, selecting an option from a menu, or rolling a die or dice. The game then switches to the next player’s turn, and so on. The game progresses in sequential order until a certain condition is met, such as reaching a goal, defeating an enemy, or running out of time. Turn-based games are different from real-time games, where events happen continuously and simultaneously. In real-time games, players require to react quickly and make decisions on the fly. In turn-based games, players have more time to think and strategize before making a move. Turn-based games are also different from hybrid games, where some elements are turn-based, and some are real-time. For example, some role-playing games use turn-based combat but real-time exploration. The origins of turn-based games? Turn-based games have a long history that can be traced back to ancient board games and tabletop games. Some of the earliest examples of turn-based games are chess, checkers, and backgammon. These games involve moving pieces on a board according to predefined rules and taking turns with an opponent. These games are still popular today and have influenced many modern video games. The first video games that used turn-based mechanics were text-based adventure games and strategy games. These games were developed in the 1970s and 1980s for personal computers and consoles. Some of the pioneers of these genres are Colossal Cave Adventure (1976), Zork (1977), Rogue (1980), and Ultima (1981). These games introduced elements such as exploration, combat, inventory management, character creation, and world-building. In the late 1980s and early 1990s, turn-based games became more popular with the rise of role-playing games and tactical games. These games combined turn-based combat with story-driven narratives and character development. It expanded the scope and depth of turn-based gameplay and introduced features such as branching paths, multiple endings, permadeath, and customization. As this genre continues to evolve, there are numbers of aspects that make a turn-based games: Tactical Decision-Making In turn-based games, victory hinges on the ability to make wise decisions in the face of uncertainty. Players must evaluate their options, analyze the game state, and anticipate their opponent’s moves. Every action becomes a calculated move in a larger chessboard, requiring strategic foresight and adaptability. This tactical decision-making element is what makes turn-based games intellectually stimulating. Roguelite games have found a special place among indie game studios due to their alignment with limited resources and the desire for replayability. Procedural generation allows indie developers to create vast and diverse game worlds efficiently, while permadeath and emergent gameplay foster discovery and personalization. The focus on gameplay mechanics enables indie studios to showcase their creativity and unique design choices, setting them apart in the competitive market. It’s worth noting that roguelite games have also attracted interest from more prominent game developers, as demonstrated by Agate’s collaboration on the game Mythic Protocol. This condition exemplifies the genre’s broad appeal and potential to captivate industry players. As the popularity of roguelite games continues to grow, we can expect more exciting and innovative titles to emerge, captivating gamers with their challenging yet rewarding experiences. Resource Management Turn-based games often incorporate resource management as a central mechanic. Players must efficiently allocate limited resources, such as currency, time, or units, to achieve their objectives. Whether it’s gathering resources, upgrading abilities, or maintaining an army, the careful management of resources becomes paramount to success. This adds another layer of complexity and strategic depth to the gameplay. Roguelite games have found a special place among indie game studios due to their alignment with limited resources and the desire for replayability. Procedural generation allows indie developers to create vast and diverse game worlds efficiently, while permadeath and emergent gameplay foster discovery and personalization. The focus on gameplay mechanics enables indie studios to showcase their creativity and unique design choices, setting them apart in the competitive market. It’s worth noting that roguelite games have also attracted interest from more prominent game developers, as demonstrated by Agate’s collaboration on the game Mythic Protocol. This condition exemplifies the genre’s broad appeal and potential to captivate industry players. As the popularity of roguelite games continues to grow, we can expect more exciting and innovative titles to emerge, captivating gamers with their challenging yet rewarding experiences. Risk and Reward Balancing risk and reward
Roguelite Games: A Blend of Challenge and Innovation

The roguelite genre has carved out a special place in the vast world of video games. With their blend of challenging gameplay, procedural generation, and permanent character death, roguelite games offer players a unique and thrilling experience. In this article, we’ll explore the key differences between roguelike and roguelite games, delve into the unique features of roguelite titles, and understand why this genre has become particularly popular among indie studios. It’s essential to understand the distinction between roguelike and roguelite games. Traditionally, roguelike games were defined by their turn-based gameplay, grid-based movement, and permanent character death, among other characteristics. These games were often known for their high difficulty, complex systems, and deep mechanics. On the other hand, roguelite games take inspiration from roguelikes but incorporate certain modifications and additions. While they retain elements like procedurally generated levels and permadeath, roguelites introduce more forgiving mechanics, such as persistent progression, unlockable upgrades, and a stronger focus on action-oriented gameplay. This subtle shift opens up the genre to a wider audience, making it more accessible and engaging for players who may not be accustomed to the extreme challenge of traditional roguelikes. Standout Features One of the standout features of roguelite games is their procedural generation. Instead of static levels, roguelites utilize algorithms to create dynamic and unique gameplay experiences with each playthrough. This results in endless possibilities, making each run feel fresh and unpredictable. Additionally, including permanent character death adds tension and excitement, as players must strategize and adapt to overcome the ever-present risk of losing progress. Another compelling aspect of roguelite games is the inclusion of persistent progression. Unlike their roguelike counterparts, roguelites often allow players to carry forward certain upgrades or abilities between runs. This sense of gradual improvement creates a satisfying sense of growth and incentivizes players to keep pushing forward, even after countless failures. It strikes a delicate balance between punishing difficulty and rewarding progression, making the experience challenging yet enjoyable. Popular for Indie Game Studio Firstly, the roguelite genre aligns well with the constraints that indie studios often face, such as limited budgets and smaller development teams. Creating a sprawling open-world game with hand-crafted content can be a monumental task for a small team. However, roguelite games leverage procedural generation to dynamically generate levels, items, and encounters. This condition significantly reduces the need for extensive manual design and allows indie developers to create vast and diverse game worlds without compromising quality. Procedural generation saves time and resources and ensures that each playthrough feels fresh and unique, enhancing replayability. Moreover, roguelite games offer a high degree of replayability, a desirable trait for indie games aiming to provide value and longevity to players. The combination of procedural generation and permadeath creates a challenging yet rewarding experience. Players face new challenges with each playthrough, discover different strategies, and unlock new content or abilities. These challenges keep players engaged and encourage them to experiment with various approaches, maximizing their enjoyment from a single game. Creating a game that can be played for hours on end without losing its appeal is a significant advantage for indie developers seeking to make a lasting impact. Additionally, roguelite games often focus on emergent gameplay and player-driven experiences. The unpredictable nature of procedural generation fosters a sense of discovery and encourages players to think on their feet, adapt to changing circumstances, and experiment with different strategies. This emergent gameplay allows players to create unique stories within the game world, providing a sense of ownership and personalization. Indie developers often strive to create games that evoke emotional connections and memorable moments, and roguelite games offer a fertile ground for players to forge their narratives. Furthermore, roguelite games prioritize gameplay mechanics and core systems over extravagant visuals or complex narratives. This focus on gameplay allows indie developers to channel their resources into creating innovative and engaging mechanics rather than investing heavily in expensive graphics or elaborate storytelling. By emphasizing gameplay, indie studios can showcase their creative ideas and unique design choices, setting their games apart from more prominent mainstream titles. This focus can help indie developers gain recognition and establish themselves in a competitive market. It doesn’t mean that only indie game studios are interested in creating roguelite games. Agate, one of the largest game developers in Indonesia, is also keen on exploring the realm of roguelite games. Their collaborative partnership demonstrates this interest in creating the game Mythic Protocol. Check out the trailer! Play Video Conclusion In conclusion, the roguelite genre has gained significant popularity in video games, offering players a unique and thrilling experience. By blending challenging gameplay, procedural generation, and permanent character death with more forgiving mechanics and persistent progression, roguelite games have widened the genre’s appeal. These games stand out with their dynamic and unpredictable gameplay, providing endless possibilities and tension. The inclusion of persistent progression creates a sense of growth and motivates players to overcome challenges. Roguelite games have found a special place among indie game studios due to their alignment with limited resources and the desire for replayability. Procedural generation allows indie developers to create vast and diverse game worlds efficiently, while permadeath and emergent gameplay foster discovery and personalization. The focus on gameplay mechanics enables indie studios to showcase their creativity and unique design choices, setting them apart in the competitive market. It’s worth noting that roguelite games have also attracted interest from more prominent game developers, as demonstrated by Agate’s collaboration on the game Mythic Protocol. This condition exemplifies the genre’s broad appeal and potential to captivate industry players. As the popularity of roguelite games continues to grow, we can expect more exciting and innovative titles to emerge, captivating gamers with their challenging yet rewarding experiences. Are you looking for co-development, art services, or game porting? Look no further than Agate! Don’t hesitate to get in touch with us today and learn more about how we can help you take your project to exceptional heights.
Mobile Game Production: The Benefits of Outsourcing
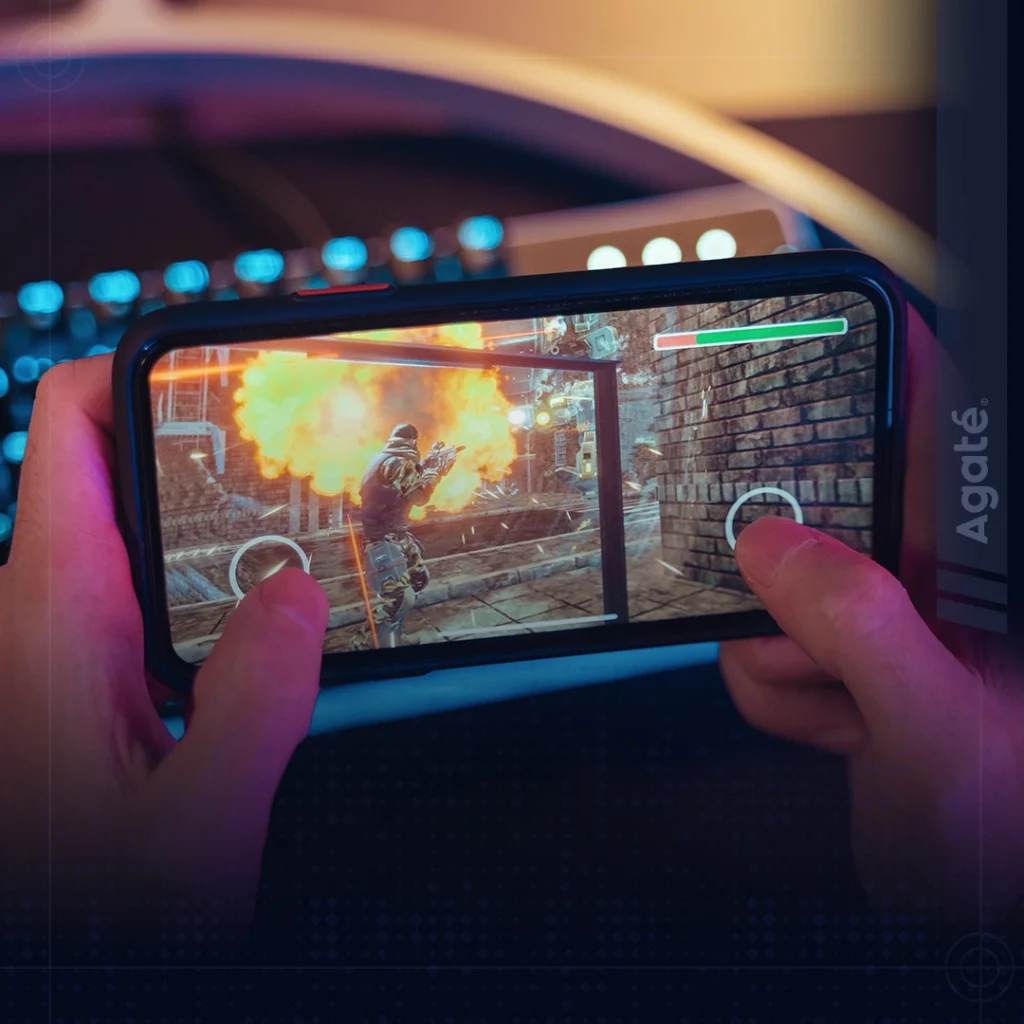

In the fast-paced world of mobile game development, staying ahead of the competition is crucial. To achieve success, many game developers are turning to outsourcing as a strategic approach. Outsourcing certain aspects of mobile game production can provide numerous benefits, allowing developers to focus on their core strengths and deliver high-quality games to the market. At Agate, we understand the importance of producing high-quality games that capture the attention of players and keep them engaged for hours on end. However, developing a mobile game from scratch can be a daunting task. That’s where outsourcing comes in. Outsourcing your mobile game production can be a game-changer for your company. It can help you save time, money, and resources while still producing a top-notch game that meets the expectations of your target audience. But when should you outsource your mobile game production, and which development phase is the best to do so? When to Outsource Your Mobile Game Production? Deciding when to outsource your mobile game production depends on several factors, such as the scope of the project, available resources, and internal expertise. Outsourcing can be particularly beneficial in the following scenarios: By around 2016, VR gaming had hit its stride with the release of notable titles. These games showcased the distinctive gameplay possibilities offered by VR, allowing players to engage with virtual objects and environments physically. Since then, the VR gaming industry has continued to thrive, boasting a growing array of games spanning various genres. Moreover, rapid technological advancements have made VR gaming more accessible and user-friendly. The birth of standalone headsets has eliminated the need for connections to powerful computers, making VR gaming more convenient and affordable. Looking ahead, the future of VR gaming appears highly promising. Ongoing advancements in both hardware and software, coupled with the integration of Augmented Reality (AR) are poised to redefine the boundaries of immersive gaming experiences. Players can anticipate even more captivating and realistic virtual worlds as VR gaming continues to evolve. Limited Internal Resources If your development team lacks the necessary skills, expertise, or bandwidth to handle certain aspects of game production, outsourcing becomes a viable option. It allows you to tap into external talent pools, access specialized skills, and leverage the experience of professionals dedicated to specific areas. Tight Deadlines When faced with demanding project timelines, outsourcing can help accelerate development. By delegating specific tasks to external teams, you can ensure a faster turnaround and meet release dates without compromising quality. Cost Optimization Outsourcing can offer cost advantages by eliminating the need for hiring and training additional in-house staff. It allows you to leverage the expertise of external teams who are already equipped with the necessary resources, saving you time and money. Development Phases Ideal for Outsourcing: Concept Art and Design: Engaging talented artists and designers to create captivating visuals, character designs, and concept art. Outsourcing this phase ensures access to creative professionals who specialize in game artistry. Programming and Development: Outsourcing programming and development tasks can expedite the coding process and ensure a robust and efficient game engine. Expert programmers can handle complex technical aspects while adhering to industry standards and best practices. Quality Assurance and Testing: Thorough testing is critical to ensure a bug-free and polished gaming experience. Outsourcing QA and testing can provide access to experienced testers who can perform comprehensive tests across different devices, platforms, and scenarios, enhancing overall game quality. Which Development Phase to Outsource Outsourcing can be beneficial at any stage of the development process, but it’s important to choose the right phase to ensure that you get the most out of your investment. Here are the three main development phases where outsourcing can be most effective: Pre-Production: Outsourcing during the pre-production phase can help you save time and money by allowing you to focus on the game’s concept and design while leaving the technical aspects to the outsourcing team. Production: Outsourcing during the production phase can help you speed up the development process and ensure that your game is released on time. Post-Production: Outsourcing during the post-production phase can help you save time and money by allowing you to focus on marketing and distribution while leaving the technical aspects to the outsourcing team. Reasons and Benefits of Outsourcing Your Mobile Game Production There are several reasons why outsourcing your mobile game production can be beneficial for your company. Here are some of the most important ones: Cost Savings Outsourcing can help you reduce development time and cost by delegating tasks to specialists who have the skills, experience, and tools to complete them efficiently and effectively. Outsourcing can also help avoid hiring and training new staff, paying for office space and equipment, or managing payroll and taxes. Improving quality and performance Outsourcing can help you improve the quality and performance of your games by accessing a pool of talented and creative professionals who can bring fresh ideas, perspectives, and solutions to the project. Outsourcing can also help developers ensure that their games meet the standards and expectations of different platforms, markets, and audiences by leveraging the expertise and knowledge of local or global partners. Time Savings Outsourcing can help you save time on development, allowing you to focus on other aspects of your business, such as marketing and distribution. Scalability Outsourcing can help developers scale up or down their production according to their needs and goals. Outsourcing can allow developers to expand their teams and capabilities when they need to handle larger or more complex projects or to reduce their teams and expenses when they need to focus on smaller or simpler projects. Outsourcing can also help developers adapt to changing market conditions and customer demands by adjusting their scope and budget accordingly. However, outsourcing also comes with some challenges and risks that developers need to consider and manage carefully, such as: Losing control and ownership: Outsourcing can make developers lose some control and ownership over their game development process, as they have to rely on external parties to deliver their work on
Discovering the Immersive World of VR Games
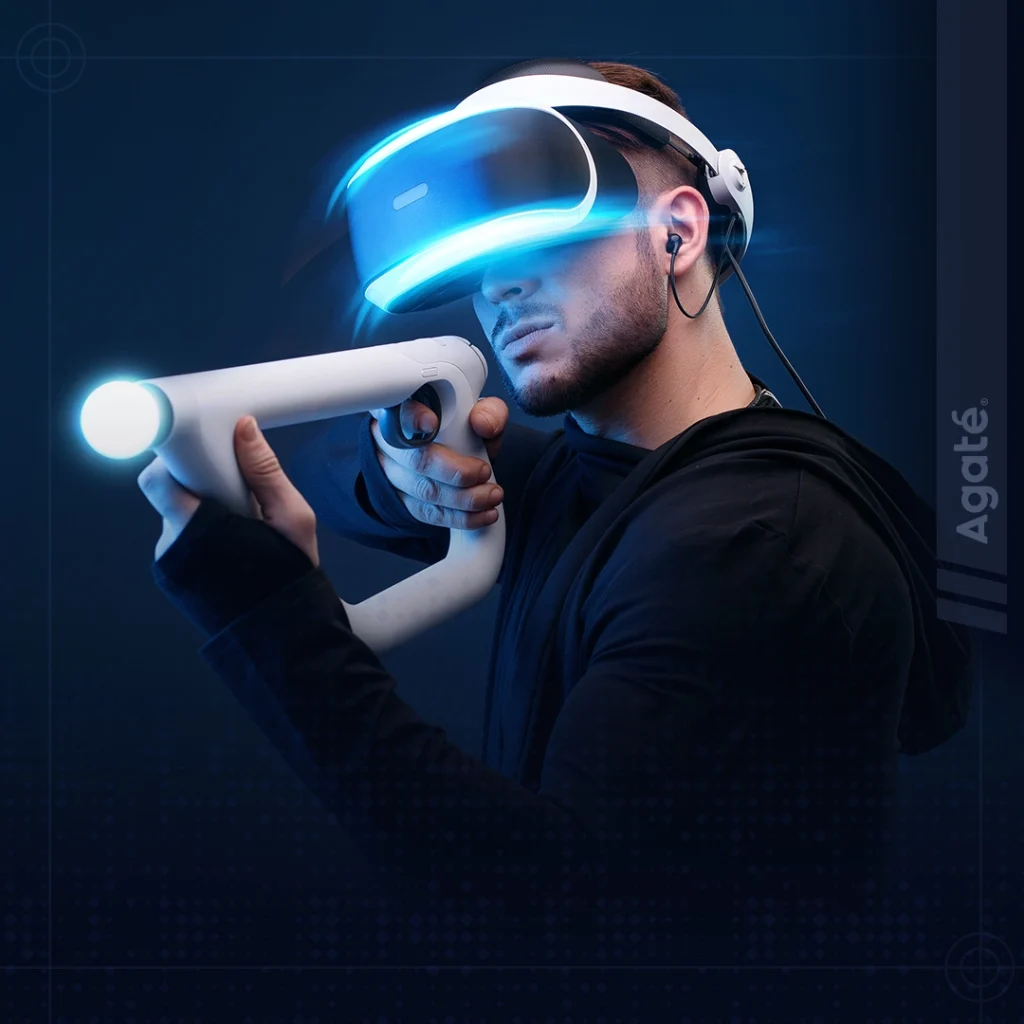

Humans have an incredible knack for innovation. One aspect of technological advancement has captured our imagination and transformed our gaming experiences: Virtual Reality (VR) games. VR gaming has revolutionized the way we engage with video games by providing an unparalleled level of immersion. It’s a technology that allows us to step into virtual worlds and experience them as if we were physically present. It’s an incredible feeling that bridges the gap between the digital and physical realms, creating a truly captivating experience. What makes VR gaming so fascinating is the ability to be fully engrossed in the game world. Every action you take in the real world is mirrored in the virtual environment, making it feel like an extension of yourself. Whether you’re wielding a virtual sword in an intense combat encounter, exploring vast virtual landscapes, or solving intricate puzzles, the level of immersion offered by VR gaming is unparalleled. As VR technology continues to evolve and improve, we can only imagine the incredible experiences that await us. The future of VR gaming holds immense potential, with ongoing advancements in hardware, software, and content creation. It’s an exciting time to be a gamer as we witness the continued growth and innovation in virtual reality. The Evolution of VR Games VR has undergone a significant evolution over the years. Initially introduced in the 1960s, it began gaining momentum in the gaming industry during the 1990s. However, the first commercially available VR headset fell short of widespread success due to limitations and high costs. Nevertheless, in the early 2010s, the arrival of headsets like Oculus Rift revitalized interest in VR gaming, offering enhanced graphics, motion tracking, and more immersive experiences. By around 2016, VR gaming had hit its stride with the release of notable titles. These games showcased the distinctive gameplay possibilities offered by VR, allowing players to engage with virtual objects and environments physically. Since then, the VR gaming industry has continued to thrive, boasting a growing array of games spanning various genres. Moreover, rapid technological advancements have made VR gaming more accessible and user-friendly. The birth of standalone headsets has eliminated the need for connections to powerful computers, making VR gaming more convenient and affordable. Looking ahead, the future of VR gaming appears highly promising. Ongoing advancements in both hardware and software, coupled with the integration of Augmented Reality (AR) are poised to redefine the boundaries of immersive gaming experiences. Players can anticipate even more captivating and realistic virtual worlds as VR gaming continues to evolve. Types of VR Games Much like games in any other medium, VR gaming offers a wide variety of types. Let’s delve into a selection of these diverse VR game types! Action: Players can immerse themselves in intense gameplay, engaging in combat, embarking on epic quests, and solving challenging puzzles in the realistic virtual environment of games. Simulation: Virtual worlds come to life, replicating real-life experiences and activities. In Simulation VR games, players can pilot planes, race cars, or even simulate different professions. Puzzle: Test your wits in intricate virtual environments of VR games, where complex puzzles must be unraveled, hidden secrets unlocked, and challenging escape rooms navigated. Horror: In this type of game, players get to experience spine-chilling virtual realms filled with jump scares, terrifying settings, and heart-pounding encounters. Sports: Sport games allow players to be active in the virtual realm with simulated sports matches, virtual workouts, and the thrill of various athletic activities. Social: Connect with friends and fellow gamers in virtual spaces designed for multiplayer interactions. Team up, strategize, and overcome challenges together in shared adventures. Exploration: Players can embark on breathtaking journeys through vast virtual worlds of games, where freedom to explore, uncover hidden treasures, and engage in thrilling adventures await. Challenges of VR Games As a technological innovation, VR gaming also faces some challenges. Here are some challenges for VR games: Hardware Requirements The hardware requirements for VR gaming remain a key consideration, as specialized equipment like VR headsets and controllers are still necessary to fully immerse oneself in the virtual reality experience. However, these components can come at a considerable cost. Furthermore, meeting the specific technical specifications for optimal performance often entails investing in high-powered gaming consoles or PCs. Limited Play Area Many VR experiences require players to have a dedicated play area to move around and interact with the virtual environment. This can be a challenge for those with limited space, making it difficult to fully engage in games that require physical movement or gestures. Content Quality and Quantity While the library of VR games has grown significantly, it is still relatively smaller compared to traditional gaming platforms. It can be challenging for developers to create high-quality and engaging content for VR due to the unique requirements of the medium. However, with the increasing popularity of VR, more developers are investing in creating compelling experiences. Accessibility and Affordability Despite advancements in technology, VR gaming can still be inaccessible to some due to high costs. The price of VR headsets and compatible hardware can be a barrier to entry, limiting the accessibility of VR games to a broader audience. Limited Multiplayer Experiences VR multiplayer games can face challenges in terms of player population and matchmaking. Since VR gaming is still a niche market, finding opponents or teammates for multiplayer games can be more challenging compared to mainstream gaming platforms. Conclusion In conclusion, VR gaming has emerged as a remarkable innovation, offering immersive and transformative experiences for players. Despite the challenges, such as hardware requirements, limited play areas, content limitations, and accessibility concerns, the growth and potential of VR gaming cannot be denied. VR gaming continues to evolve and captivate players with its ability to transport them to fantastical realms, provide intense gameplay, and create a sense of presence like never before. As the industry progresses, overcoming challenges and embracing new technologies, VR gaming is said to reshape the way we experience and interact with video games, unlocking unprecedented levels of immersion and enjoyment. Are you looking
Web3 Games: Can We Start Today?

Over the past few years, the world of gaming has undergone a significant transformation. With the advent of blockchain technology, the gaming industry has been revolutionized, and a new era of gaming has emerged, and it is Web3 games. We have all been promised a utopia where we can make money by playing games and, at the same time, provide jobs through games in the world of web3. This huge phenomenon has been getting all the buzz, from developers to players and non-players worldwide. However, things have not turned out as we had hoped. The question is, can we start making web3 games? The answer is yes, and here’s why! The Promise of Web3 Games Web3 games offer a new level of ownership and control for players. Unlike traditional games, where players are subject to the rules and restrictions imposed by game developers and publishers, Web3 games allow players to own their in-game assets and characters as non-fungible tokens (NFTs) on the blockchain. This means that players can trade, sell, or lend their NFTs to other players or platforms without any intermediaries or fees. Moreover, players can also participate in the governance and decision-making of the game through decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs), where they can vote on game updates, features, and policies. Web3 games provide a new source of income and opportunity for players. By playing Web3 games, players can earn cryptocurrencies or tokens that can be exchanged for real money or other digital assets. Some Web3 games also reward players for contributing to the game development or community, such as creating content, providing feedback, or promoting the game. Additionally, Web3 games enable players to access a global and open market where they can find new audiences, partners, and collaborators for their gaming activities. These types of games foster a new culture of innovation and creativity for developers. With Web3 games, developers can leverage the power and potential of blockchain to create novel and immersive gaming experiences that aren’t possible with traditional platforms. For instance, developers can use smart contracts to create dynamic and interactive game logic that can adapt to the player’s actions and choices. Developers can also use decentralized storage and computation networks to ensure the security and scalability of their game data and logic. Furthermore, developers can benefit from the network effects and interoperability of Web3 games, where they can integrate their games with other platforms and protocols to enhance their game features and functionality. The Reality of Web3 Games While the promise of Web3 games is exciting, the reality is that the industry is still in its early stages. There are only a few Web3 games available, and they are not as popular as traditional games. The reason for this is that they are still relatively unknown, and many people are hesitant to try them out. Additionally, the games are still in development, and there are many bugs and glitches that need to be fixed. Can We Start Making Web3 Games? The answer is yes. Despite the recent controversy over the future of web3, many developers and enthusiasts have moved past it and continue to pursue their vision of a more open and fair gaming industry. There are already some examples of successful web3 games that show the potential and benefits of web3 gaming, such as creating new revenue streams for players and developers, fostering community engagement and governance, and enabling new forms of gameplay and creativity. However, it requires a lot of knowledge and expertise. It requires a lot of knowledge and expertise in various fields, such as cryptography, smart contracts, game design, user experience, and scalability. Developers need to have a deep understanding of blockchain technology and decentralized platforms. They also need to be familiar with programming languages such as Solidity, which is used to create smart contracts on the Ethereum blockchain. Creating a Web3 game is not an easy task, but it’s possible for those who are willing to put in the time and effort. One of the ways to overcome the challenges of making web3 games is to form strategic partnerships with other developers and publishers who share the same vision and goals. By collaborating with others, web3 game developers can leverage their combined resources, expertise, and networks to create more innovative and engaging games that appeal to a wider audience. Moreover, partnerships can help web3 game developers to access existing platforms and ecosystems that support web3 gaming, such as blockchain protocols, wallets, marketplaces, and communities. The Future of Web3 Games The future of Web3 games is promising. As the industry continues to grow, we can expect to see more games being developed and more players joining the Web3 gaming community. The potential for earning cryptocurrency while playing games is a significant draw for many players, and it is likely that this trend will continue to grow. Additionally, as technology improves, we can expect to see more advanced and sophisticated Web3 games being developed. Conclusion Web3 games are not just a hype or a fad. They are a paradigm shift that will redefine the gaming industry and create new value and opportunities for both players and developers. Web3 games have ushered in a new era of gaming, offering players ownership, control, and new sources of income. These games provide players with the ability to own in-game assets as NFTs on the blockchain, trade them freely, and participate in game governance through DAOs. Players can also earn cryptocurrencies or tokens by playing Web3 games, contributing to game development, or engaging with the community. For developers, Web3 games unlock a realm of innovation and creativity by leveraging blockchain technology to create immersive gaming experiences and tap into network effects and interoperability. However, the industry is still in its early stages, with limited availability and popularity compared to traditional games. Despite the challenges, many developers and enthusiasts are actively pursuing their vision of a more open and fair gaming industry. Strategic partnerships can help overcome these challenges by combining resources and expertise.
Work-Life Balance: A Step Towards Better Crews Well-being

The gaming industry is no stranger to long hours and tight deadlines. With its endless desire for breakthroughs, it becomes a landscape of invention and dedication that frequently challenges the limits of its experts. However, beneath the exciting challenges and rewarding accomplishments lies a hidden concern: work-life balance. Now, imagine achieving a high score, not just in any game, but in the ultimate game: life itself! Strap in as we embark on an insightful exploration into the essence of work-life balance and its crucial role in well-being. This article is your gateway to understanding how Agate is stepping up its game and supporting its crew in achieving that golden equilibrium. Understanding Work-Life Balance Work-life balance refers to an individual’s ability to distribute time and energy between work and personal obligations evenly. This equilibrium is crucial for mental and physical health, as well as the overall quality of life [1]. Achieving a healthy work-life balance doesn’t necessarily mean an equal division of hours between work and personal life but rather finding a flexible and functional equilibrium that suits individual needs and lifestyles. In essence, it’s about having the autonomy to juggle professional responsibilities and personal commitments efficiently. The Importance of Work-Life Balance and Its Impact on Crew’s Well-Being In the gaming industry, the continuous striving for innovation often leads to intense schedules. Over time, this lack of balance can lead to burnout, decreased productivity, and negative impacts on employees’ physical and mental health [2]. Contrarily, a healthy work-life balance can boost morale, productivity, and overall employee well-being [3]. At its core, employee well-being is linked to how valued and supported employees feel within the workspace. At Agate, we place a high value on our crews’ well-being. We have implemented regular well-being checkups, conducted monthly, and a comprehensive burnout and well-being survey every six months. Our Talent Team (HR) carefully evaluates the results, providing support to crews and helping them navigate any challenges they may face. Follow up well-being issue How to Foster Good Work-Life Balance Take Worthwhile Breaks Evaluate if your break activities genuinely bring happiness, contribute to your health, or strengthen social bonds rather than simply acting out of habit. Aim for mindful leisure choices since mindlessly browsing social media tends to decrease happiness. In essence, taking deliberate breaks can boost your productivity and overall well-being [4]. Boost Your Work Efficiency Evaluate how you allocate work time. Can you delegate some tasks? Can you simplify routine jobs or minimize daily minor decisions? Consider blocking off time for important projects without a set deadline so they don’t fall through. Need to focus? Try turning off phone and email alerts temporarily. Remember, even a notification sound can be as distracting as using your phone [5]. Flexible Work Schedules Having flexible work schedules can give employees more control and autonomy, and research suggests that this policy can increase productivity [6]. People with flexible schedules take fewer sick days, experience less work-related impairment, and are more committed to their jobs. Pace, Space, Place Remember the three Ps in an ever-changing work environment. Set your own PACE, avoid rushing, and take regular rests. Choose your PLACE wisely, select a relaxing and stimulating environment to work in. Finally, respect your SPACE by keeping it tidy and conducive to concentrate. This trio has the potential to be your secret weapon against burnout! [7] Promoting work-life balance goes beyond just flexible schedules. It’s about creating an environment that promotes growth, fun, and relaxation. One strategy we employ at Agate is team building, a fun monthly event where Agate crews participate in various activities ranging from board games to community meals. These gatherings foster stronger connections and enhanced synergy among our dynamic crews. But our commitment to balance continues. Expanding on the concept of team building, this is where Agate Clan comes into play. Agate Clan is a collection of various extracurriculars that each crew can join according to their interests. These clans range from sports like the Badminton Clan to Art Clan, offering a diversity of activities that help our crews to wind down, learn something new, or simply enjoy a shared passion. They also serve to ensure our team members have a balanced life that caters to their personal interests and well-being. Agate Clan Nothing can illustrate the positive impact of work-life balance at Agate better than the real experiences of our crews. Let’s hear it from our crews who’ve found an exciting balance in their lives at Agate! Agate Futsal Clan “To me, work-life balance means achieving harmony between earning a living and engaging in fulfilling personal activities that keep us healthy, happy, and stress-free. Each person may have different proportions of this balance, but I firmly believe that excessive indulgence in any aspect isn’t beneficial. Work-life balance is of utmost importance. It’s no secret that mental health impacts our physical health, and with a healthy mind and body, we can deliver better work quality. Joining the AFC was a no-brainer. I’ve always had a penchant for football. Additionally, being somewhat passive in social settings, the AFC has provided a platform for me to interact with colleagues from different teams in an unforced manner. Participating in AFC has brought multiple benefits to my well-being. I have noticed significant improvements in my physical health, and it’s helped to alleviate feelings of isolation, especially after the recent pandemic. Joining AFC felt like a breath of fresh air!” Nelson playing mini soccer Agate Fustal Clan Agate Gunpla Clan “For me, achieving a good work-life balance is about having a mutually supportive system. Your work and personal life should complement each other, leading to overall satisfaction and well-being. Maintaining this balance is crucial, as it ensures continued enjoyment of life and work. Remember, even activities you love can lead to burnout if done in excess. My love for creation and modification, spanning from Legos to robotics, naturally led me to Gunpla and plastic models. When I discovered the interest of Gunpla at Agate, I saw the chance to unite people
Co-Development: The Future of Video Game Production?

Co-development has been common in the video game business for a long time. Although outsourcing in any form of content in video game development was once considered a bad thing, it has been recently considered beneficial for all parties. Its impact has increased significantly in recent years as triple-A games have become larger and more complex. You might have noticed that some of the most popular titles in recent years have been developed by more than one studio. This is one of the many reasons why today, Agate has spread its services to co-development. Co-development can take many forms, such as outsourcing, joint ventures, partnerships, or alliances. But for those who aren’t aware, let’s find out what co-development in game development really is! What is Co-Development? Co-development is when two or more studios collaborate to make a video game. They can share their resources, skills, and technologies to make a game that is better than what they could do alone. Co-development can have different forms, such as two studios working on separate parts of the game or a bigger team of studios working on everything together. Co-development has been a common practice in the video game industry for many years, but it has gained more traction in recent times. This is because modern video games have become increasingly complex, and it’s challenging for a single studio to handle all aspects of game development. Co-development allows studios to focus on their strengths and work together to create a complete game that is of high quality. It also helps to reduce the risk and uncertainty associated with developing a game alone, as studios can share the costs and resources required to create a game. Why is Co-Development Becoming More Popular? The video game industry is seeing more co-development for several reasons. One reason is that modern video games are very complex. It is hard for one studio to do everything by itself. Co-development lets studios focus on what they are good at, such as graphics or gameplay, and work together to make a complete game. Another reason is that video games are very expensive to make. It can cost millions of dollars to make a high-quality game, and many studios don’t have enough money to do it on their own. Co-development helps studios split the costs of making a game, making it easier to make high-quality games without spending too much money. Lastly, co-development helps studios learn from each other and improve their own skills. By working together, studios can benefit from each other’s strengths and expertise. This can lead to better games and faster development times. What are the benefits of co-development? It allows studios to share resources, expertise, and technology, which can improve the quality and scope of the game. It enables studios to access new markets, audiences, and platforms, which can increase the sales and reach of the game. It fosters innovation and creativity, as studios can learn from each other and experiment with new ideas and genres. It reduces risk and uncertainty, as studios can mitigate the challenges and costs of developing a game alone. However, co-development also comes with some challenges, such as: It requires clear communication, coordination, and trust among the studios involved, which can be difficult across different cultures, languages, and time zones. It involves sharing intellectual property rights, revenue, and control over the game, which can create conflicts and disputes among the studios. So, is co-development the future of video game production? There is no definitive answer to this question, as different studios have different goals, preferences, and strategies. Even so, there are more pros than cons when it comes to co-development, especially in making games. What is certain is that co-development is a growing trend in the video game industry that offers plenty of opportunities for all parties in game development. What does co-development offer? There are several types of co-development, depending on the company that offers such services. A company may only have a part of video game development, some have a few services to offer, and some may have several services. At Agate, we offer full-cycle development, art, and porting services for co-development projects. Full-cycle development means that Agate can handle all aspects of game creation from concept to launch. Art service means that Agate can create high-quality art assets for games, such as 2D and 3D graphics, animations, UI, and VFX. While porting service means that Agate can adapt games to run on different platforms, such as PC, consoles, mobile, and VR. With around 300 team members who are experienced in both Unreal Engine and Unity, Agate can deliver exceptional games that can cater to the needs of all clients that require such services from Agate. As technology evolves and consumer expectations rise, co-development might become more prevalent and essential for creating a plethora of gaming experiences. Conclusion Co-development is becoming increasingly popular in the video game industry due to the complexity and cost of creating high-quality games. Co-development allows studios to share resources, expertise, and technology, which can improve the quality and scope of the game, access new markets and platforms, foster innovation and creativity, and reduce risk and uncertainty. However, co-development also comes with challenges such as clear communication, coordination, trust among the studios involved, and sharing intellectual property rights, revenue, and control over the game. While there is no definitive answer to whether co-development is the future of video game production, it is a growing trend that offers plenty of opportunities for all parties involved in game development. Companies like Agate offer various co-development services, including full-cycle development, art, and porting services, to cater to the needs of clients in the industry. As technology evolves and consumer expectations rise, co-development may become more prevalent and essential for creating a wide range of gaming experiences. Are you looking for co-development, art services, or game porting? Look no further than Agate! Don’t hesitate to get in touch with us today and learn more about how we can
Exploring the Vast World of Game Genres

What if you can only play one game genre for the rest of your life? While it’s totally understandable to have an all-time favorite game genre, we should all appreciate the incredible variety of genres available in the gaming industry. The world of video games is a fascinating place that knows no bounds. From the adrenaline-fueled excitement of first-person shooters to the immersive storytelling of role-playing games, each genre provides a distinctive and captivating experience that enthralls players from all walks of life. Within the expansive gaming realm, video game genres hold a special place as the building blocks that shape the diverse and ever-evolving gaming landscape. These genres serve as the foundation upon which developers craft their immersive experiences, allowing players to embark on unique adventures and explore distinct gameplay mechanics. Why It’s Important Catering to Diverse Player Preferences Video game genres cater to players’ diverse interests and preferences, ensuring there is something for everyone. Each genre has its distinct appeal, resonating with different types of players based on their preferences and playstyles. Whether it’s the adrenaline-fueled action of first-person shooters, the strategic depth of real-time strategy games, or the immersive narratives of role-playing adventures, genres provide a means for players to find experiences that align with their tastes. From casual gamers seeking lighthearted entertainment to competitive enthusiasts craving intense challenges, genres offer various options to cater to a wide range of player preferences. Player Engagement Well-designed game mechanics are essential for capturing and maintaining player interest. Game mechanics keep players invested in the gameplay by providing engaging challenges, meaningful choices, and rewarding feedback. Whether mastering a tricky combo in a fighting game or strategizing resource allocation in a simulation game, compelling mechanics create a sense of accomplishment and encourage players to continue playing. Defining Gaming Experiences Within the realm of video games, genres play a pivotal role in shaping the gaming experiences that players embark upon. Each genre offers a unique combination of gameplay mechanics and storytelling techniques, creating distinct and memorable encounters. From the heart-pounding action sequences of action games to the thought-provoking narratives found in adventure games, genres set the stage for immersive and captivating experiences. They introduce genre-specific elements that contribute to the overall appeal, such as the vast open worlds of exploration, the ability to customize characters to reflect individual identities or the intricate puzzle-solving challenges that engage players’ problem-solving skills. Through these defining features, genres establish a sense of identity and create a bond between players and the games they love. Influencing Industry Trends Certain video game genres’ popularity and influence have profoundly impacted industry trends and market demand. Genres have evolved and risen to prominence over time, shaping the trajectory of game development. The success of specific genres has not only influenced the creative direction of future games but has also impacted the business models and strategies employed by game publishers and developers. As genres capture the hearts and minds of players, game studios adapt to meet the demands of the market, leading to the emergence of new studios specializing in specific genres, the rise of genre-specific conventions and events, and the implementation of innovative monetization models. Genre trends continue to drive the gaming industry’s evolution, shaping how games are developed, marketed, and consumed. By exploring the multifaceted role of video game genres in fostering creativity, catering to player preferences, defining gaming experiences, and influencing industry trends, we gain a deeper appreciation for the impact these genres have on the gaming landscape. Their significance extends beyond mere categorization, as they provide the building blocks for unforgettable gaming experiences and shape the ever-evolving world of interactive entertainment. The Evolution of Game Genre If traced back to the earlier days, the origins of video game genres began when developers were exploring different types of gameplay experiences. As the medium evolved, it led to the establishment of distinct genres. Tracing the origins of video game genres involves examining the early pioneers and their contributions to shaping the landscape of interactive entertainment. One of the earliest and most influential genres to emerge was the text-based adventure game. These games relied on text commands for interaction and presented players with interactive stories and puzzles to solve. This genre later evolved into graphical adventure games, which utilized visuals and point-and-click interfaces. Another early genre that had a significant impact on video game development was the maze or dungeon crawler genre. These games introduced first-person perspectives and exploration of labyrinthine environments. Later, these games became the foundation for future genres such as first-person shooters and role-playing games. The action genre also emerged early in video game history. Games introduced fast-paced gameplay and shooting mechanics. These games inspired the development of various subgenres within the action genre, including shoot ’em-ups, run-and-gun games, and platformers. The platformer genre gained popularity and featured a protagonist navigating platforms, jumping over obstacles, and defeating enemies. The success of these games led to the development of countless platformer titles, making it one of the enduring genres in video game history. As the industry progressed, additional genres emerged, influenced by a combination of technological advancements, player preferences, and innovations by game developers. The role-playing game (RPG) genre expanded, offering deeper narratives, character progression systems, and strategic turn-based combat. These early genres formed the basis for the rich and diverse range of genres we see in modern video games. Over the years, countless subgenres and hybrids have emerged, combining elements from different genres and pushing the boundaries of interactive entertainment. The Future of Game Genre The future of video game genres holds exciting possibilities for innovation and evolution. As technology continues to advance and player expectations evolve, we can speculate on potential directions for genre design. Here are a few possibilities: Hybrid Genres Play Video Valthitian Arc: Hero School Story 2 Trailer The blending of genres presents an exciting opportunity to create innovative gameplay experiences that deliver a fresh and unique encounter for players. By skillfully combining the finest elements from
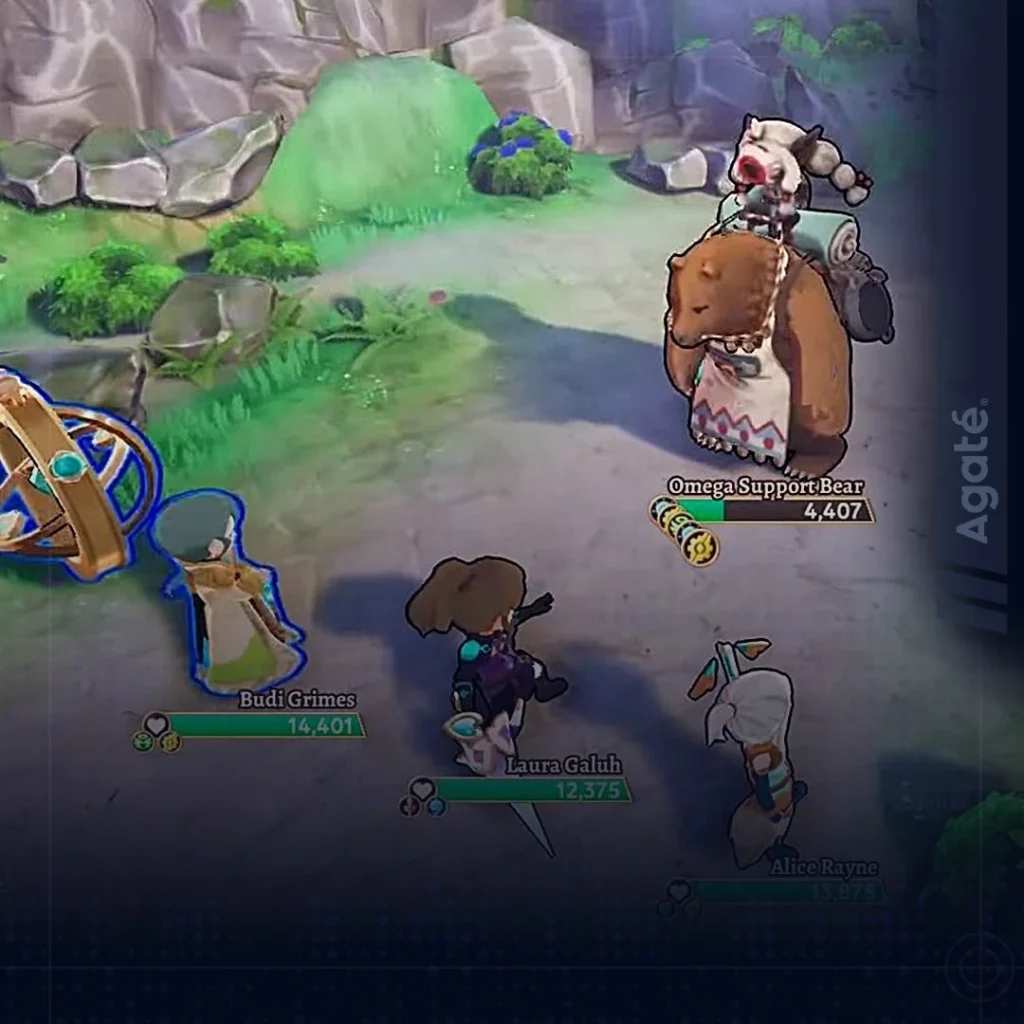
Game Mechanics: Crafting Immersive Experiences

In the vast world of video games, a crucial element is the backbone of every interactive experience: game mechanics. Game mechanics encompass the rules, systems, and interactions that define how a game is played. They determine the actions players can take, the challenges they face, and the goals they strive to achieve. From the simplest mobile games to the most complex open-world adventures, game mechanics shape the gameplay experience. Game mechanics consists of a wide range of elements, including movement controls, combat systems, character progression, resource management, puzzles, and much more. These mechanics work harmoniously to create a cohesive and engaging experience for players. They form the underlying structure that brings the game world to life, enabling players to explore, overcome obstacles, and experience a sense of achievement. Why is Game Mechanics Important? Game mechanics play a pivotal role in shaping a video game’s overall quality and appeal. Here are several reasons why game mechanics are of utmost importance in the world of gaming: Player Engagement Well-designed game mechanics are essential for capturing and maintaining player interest. Game mechanics keep players invested in the gameplay by providing engaging challenges, meaningful choices, and rewarding feedback. Whether mastering a tricky combo in a fighting game or strategizing resource allocation in a simulation game, compelling mechanics create a sense of accomplishment and encourage players to continue playing. Balancing Challenge and Reward Effective game mechanics strike a delicate balance between challenge and reward. The mechanism creates a satisfying gameplay loop by offering progressively more challenging tasks and matching them with appropriate rewards. This balance ensures that players are consistently challenged without becoming frustrated, fostering a sense of progression and accomplishment as they overcome obstacles and achieve goals. Immersion and Player Agency Game mechanics allow players to immerse themselves in a virtual world and exercise their agency. When mechanics are intuitive, responsive, and consistent, they provide a sense of control and empower players to make decisions that directly impact the game’s outcome. This immersion enhances the player’s emotional connection to the game, making the experience more memorable and enjoyable. Driving Narrative and Player Experience Game mechanics can be instrumental in driving the narrative and shaping the player’s experience. Players can actively influence the game’s plot and character development through mechanics like dialogue choices, branching storylines, and moral decision-making. This interplay between mechanics and storytelling immerses players in a rich narrative and allows for personalized experiences, increasing the game’s replayability and longevity. Fostering Competition and Social Interaction Game mechanics often serve as the foundation for multiplayer experiences, fostering competition and social interaction among players. Whether through leaderboards, cooperative gameplay, or player-versus-player encounters, well-designed mechanics encourage healthy competition, teamwork, and the formation of online communities. These mechanics provide opportunities for players to collaborate, strategize, and challenge one another, further enhancing the overall gaming experience. Here are some examples of the unique game mechanics implementation. Code Atma Code Atma is one of the mobile games produced by Agate. In this game, players will control mystical creatures from Indonesian mythology, called “atma,” and create a team of 6 atmas to defeat enemies. Each atma has active and passive abilities, from dealing damage to enemies, providing status buff or debuff, or performing healing. Active abilities are abilities that players activate, while passive abilities become active when certain conditions are met. For example, if an atma receives healing, it will provide a speed buff to other atmas. These passive abilities challenge players to find the best strategies for utilizing atmas that can take advantage of each other’s passive abilities. The game allows players to choose the best plan, with dozens of atmas, each possessing unique abilities. Check the gameplay trailer here. Play Video Play Code Atma on your device! Valthirian Arc: Hero School Story 2 Valthirian Arc: Hero School Story 2 is another game produced by Agate that can be played on PC and Nintendo Steam, currently in early access. The game combines RPG and management genres, where players take on the role of a school principal in a hero academy. Each year in the game, players receive students with different backgrounds and unique abilities, and players decide which lessons are suitable for the students, based on the available school facilities. The lessons they receive will improve their abilities and unlock skills they can use in battles. The school you manage will receive job requests from 4 factions, which can be completed by sending students to finish those jobs. The battle system in this game is also different from other turn-based RPGs. Typically, each character takes turns attacking, but in this game, players can determine which character they want to use on their turn. So, if the player focuses on attacking, they can continuously use characters with the best-attacking abilities to defeat enemies. This freedom provides a new dimension for players to determine the right strategies in combat. By completing quests, the academy will receive reward resources that can be used for upgrades or for constructing new facilities in the academy. The more facilities that are built, the more academy can unlock students’ potential. As more potential students are opened, they become stronger and can take on more challenging quests, and harder quests provide more significant rewards. This gameplay loop makes Valthirian Arc: Hero School Story 2 beloved by its players. Check the trailer here. Play Video This game is planned to be fully released later this year. Play the early access now! Conclusion In conclusion, game mechanics form the foundation of interactive experiences, determining how players navigate and interact with virtual worlds. From promoting engagement and immersion to fostering competition and driving narratives, game mechanics are vital in creating compelling and unforgettable gaming experiences. By understanding and harnessing the power of game mechanics, developers can craft games that captivate players and leave a lasting impression in the ever-evolving landscape of the gaming industry.
Exploring the Impact, Challenges, and Future of AAA Games

In recent years, AAA games have experienced a meteoric rise in popularity, captivating the hearts and minds of gamers worldwide. These blockbuster titles, known for their high production values, immersive gameplay, and cutting-edge technology, have driven the gaming industry’s unprecedented growth. With each passing day, AAA games keep pushing boundaries, captivating new audiences, and redefining the gaming landscape. As the popularity of AAA games continues to soar, they profoundly impact various aspects of the gaming industry. Let’s explore the impacts, challenges, and future of AAA games! Economic Impacts Generating Revenue and Sales Figures As AAA games continue to captivate audiences worldwide, their impact on revenue generation and sales figures cannot be overstated. These games serve as major contributors to the gaming industry’s growth and hold the potential to create a significant influence on a country’s economy as a whole. A recent study by the Entertainment Software Association (ESA) revealed that the video game industry contributes an impressive $90.3 billion in annual economic output and supports approximately 429,000 jobs nationwide. These findings show the immense economic impact that AAA games can have. Influence on Hardware and Software Sales The impending release of a highly anticipated AAA game has a remarkable impact on hardware and software sales. For instance, when a highly anticipated game is announced, gamers worldwide are filled with excitement and anticipation. They start considering their gaming setup and often decide to upgrade their existing consoles, invest in powerful gaming computers, or even purchase dedicated gaming accessories like high-performance controllers or immersive headsets. The surge in demand for these gaming devices drives up sales and creates a thriving market for hardware manufacturers and retailers. Moreover, the excitement surrounding the AAA game release translates into a surge in software sales. Players eagerly pre-order the game, ensuring they have access to it as soon as it becomes available. The anticipation and hype generate a buzz in the gaming community, leading to an increase not only for the game but also for related software such as expansion packs, downloadable content, and in-game purchases. Additionally, players may invest in accessories like gaming mouse or gaming chairs to enhance their overall gaming experience. Job Creation and Economic Growth The AAA game industry plays a vital role in job creation and contributes substantially to economic growth. The development of AAA games requires a diverse range of skilled professionals, including game designers, programmers, artists, writers, and many others. As the industry continues to expand, the demand for talented individuals in these fields increases, leading to a surge in job opportunities. This not only benefits those directly involved in game development but also extends to related sectors such as marketing, distribution, and technical support services, creating a ripple effect of employment opportunities. The economic impact of the AAA game industry goes beyond job creation. It encompasses various aspects of the economy, including increased investments, technological advancements, and revenue generation. The success of AAA games leads to significant revenue streams, with sales reaching impressive figures. This revenue not only fuels the growth and development of game studios but also contributes to the overall economic health of the country or region. Furthermore, the AAA game industry has a positive impact on related sectors, such as retail, e-commerce, and tourism. The release of highly anticipated AAA games often drives consumers to purchase gaming consoles, accessories, and merchandise, boosting sales in the retail sector. Online platforms and e-commerce websites experience increased traffic and transactions as players seek to acquire the latest games and gaming peripherals. Additionally, the popularity of AAA games attracts tourists and visitors to gaming conventions, tournaments, and events, stimulating local economies and generating revenue in the tourism sector. Cultural Impact In recent years, the gaming industry has become increasingly aware of the importance of representation and diversity. AAA games, with their huge global player base, are right in the spotlight when it comes to diversity and representation in gaming. It’s not just about the people making the games but also about the characters we see in those games, representing all aspects of diversity, such as genders, abilities, etc. Considering the vast number of players involved, it is crucial to acknowledge the significance of proper representation and inclusive diversity in creating a more authentic virtual world that mirrors the diverse nature of our society. However, there remains a notable lack of diverse representation in AAA games. For instance, based on an analysis of the top-selling and major games released since 2017, it was found that nearly 80 percent of the main characters are male, and approximately 55 percent are of white ethnicity. Although there has been some improvement in representation, it is often presented as optional or additional content rather than being seamlessly integrated into the core gameplay. This approach significantly impacts people’s perceptions and shapes their viewpoints. With the increasing awareness of this issue, there is a significant opportunity for AAA games to make a positive impact on society. By placing a strong emphasis on diversity and embracing the uniqueness of individuals within their primary game experiences, they have the power to promote understanding, foster tolerance, and champion inclusivity in pop culture. Challenges Diversity and Representation While AAA games have made significant progress in this issue in recent years, there is still room for improvement when it comes to diversity and representation in games. Hopefully, in the future, more AAA games can accurately and inclusively represent the diversity of our society. Crunch Culture and Its Impact on Developers Crunch culture, which refers to working excessively and continuously to meet tight deadlines, is a severe challenge for AAA game developers. The demand to launch games within a short timeframe often results in immense pressure on the development team, which can negatively impact their health and well-being. Balancing Innovation with Commercial Finding a balance between innovation and commercial AAA games is another challenge. While developers want to bring fresh and innovative experiences to players, commercial aspects also need to be considered for the game to achieve financial success. Future of

